What is Regenerative Medicine?
– Stem Cell Therapy
Regenerative Medicine is a new field of medicine and is focused on developing and applying new treatments to heal tissues and organs and restore function lost due to aging, disease, damage or defects.
The human body has the natural ability to heal itself in many ways. A cut to the skin repairs itself, broken bones mend and a living-donor’s liver regenerates in a few weeks. Imagine if scientists could capture this naturally occurring ability to heal and apply it to a wide range of conditions.
Stem cell therapy is a form of regenerative medicine designed to repair damaged cells within the body by reducing inflammation and modulating the immune system. This phenomenon makes stem cell therapy a viable treatment option for a variety of medical conditions. Stem cell therapies have been used to treat autoimmune, inflammatory, neurological, orthopedic conditions and traumatic injuries with studies conducted on use for Crohn’s disease, Multiple Sclerosis, Lupus, COPD, Parkinson’s, ALS, Stroke recovery and more.
What are Mesenchymal stem cells?
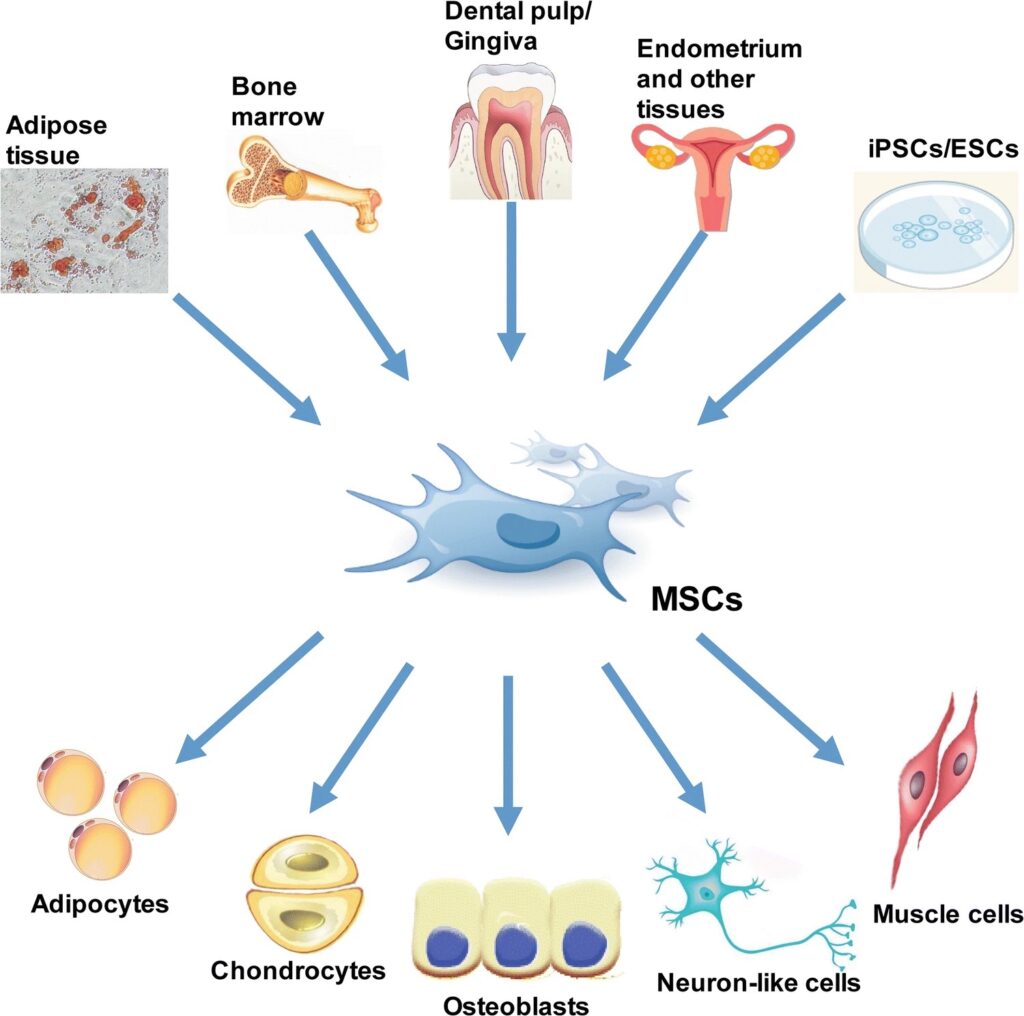
Mesenchymal stem cells are adult stem cells that have self-renewal, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, signaling, and differentiation properties. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), self renewal capacity is characterized by their ability to divide and develop into multiple specialized cell types present in a specific tissue or organ.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be sourced from a variety of tissue including adipose tissue (fat), bone marrow, umbilical cord tissue, blood, liver, dental pulp, and skin.
How does Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy work?
Mesenchymal stem cells utilize their self-renewal, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, signaling, and differentiation properties to influence positive change within the body. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) also have the capacity to self-renew by dividing and developing into multiple specialized cell types present in a specific tissue or organ.
Stem cells have a unique, intrinsic property that attracts them to inflammation in the body. Studies have shown that stem cells can regenerate damaged or diseased tissues, reduce inflammation and modulate the immune system promoting better health and quality of life. Mesenchymal stem cells do this by influencing tissue repair via paracrine effects (cell signaling in order to change the behaviour of existing cells) or direct cell-to-cell contact.

